In the SN2 reaction the nucleophile attacks from the most δ region. Measurement error for volumes or masses.
Behind the leaving group.

. This is called a back-side attack. ΔG ΔG0 RT lnQ where Q is the ratio of concentrations or activities of the products divided by the reactants. If a chemical equation is reversed then Grxn changes sign.
Rxn One point is earned for an answer with justification consistent with the answer in part c. The figure below shows the relationship between G for the following reaction and the logarithm to the base e of the reaction quotient for the reaction between N 2 and H 2 to form NH 3. E Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for the reaction at 298 K.
A negative value for Δ G indicates a spontaneous process. Not 298K or if more or less than one mole of carbon is consumed in the reaction then a value of G rxn will differ from G rxn. Write a set of reactions such as those given showing how the glutamate and ammonia reaction can couple with the hydrolysis of ATP.
Gibbs free energy is denoted by the symbol G. Im just a little confused about these two things. The spontaneity of a chemical reaction changes when G rxn 0.
Concentration of Aqueous solutions are 1. IF so then the reaction will need to from more reactants reduce the value of Q and allow G to reach zero ie allow equilibrium to be established. A negative G also means that the products of the reaction have less free energy than the reactants because they gave off some free energy during the reaction.
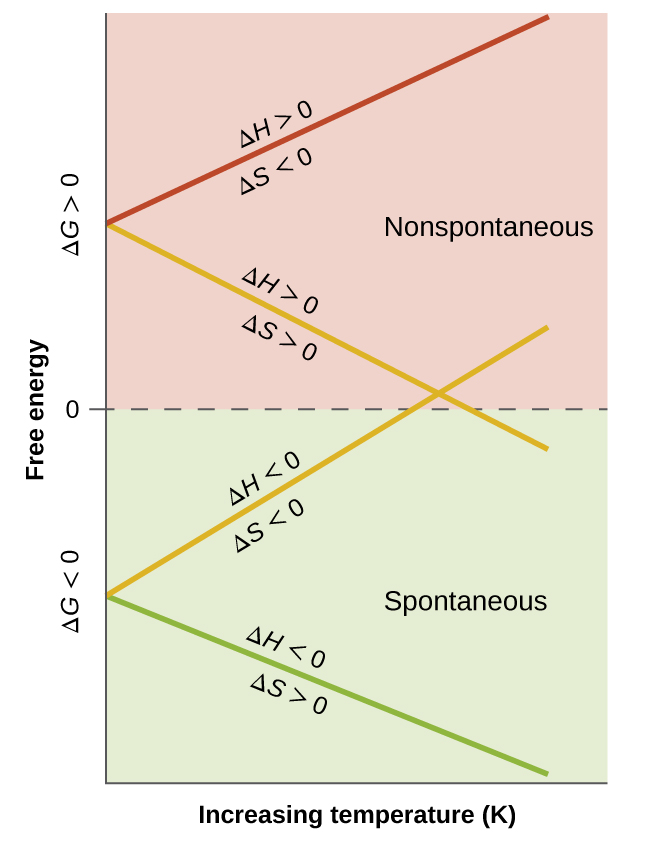
Unless H rxn and S rxn have different signs the spontaneity of a reaction is temperature dependent. Compare and contrast these standard values. The S N 2 Reaction Notes.
Grxn and o S rxn Key Questions 6. ΔG rxn rxn is calculated using only enthalpy. A positive Δ G indicates a nonspontaneous process.
If you want to calculate ΔG under non-standard conditions you need to use the equation. When Δ H rxn is positive and Δ S rxn is negative. So standard gifts Reino de Delta G is the difference between product minus that off reacted.
The standard free energy change for the reaction is 142 kJmol. Δ G rxn depends on the values of both Δ H rxn and Δ S rxn. Rxn is calculated using enthalpy and entropy whereas ΔG rxn is calculated using only enthalpy.
The dissolution of each salt. Under standard conditions when Q 1 the reaction is spontaneous in the reverse direction. Use Hfº and Gfº data in your textbook to calculate Hrxn and Grxn for.
For which conditions for Δ H rxn and Δ S rxn will a reaction always be spontaneous under standard conditions. This problem has been solved. In other words it is the difference between the free energy of a substance and the free energies of its constituent elements at standard-state conditions.
ΔG rxn rxn is calculated at any point in the reaction at non-standard conditions. If G is positive at equilibrium then we will have lots of reactants at equilibrium meaning Q needs to. The maximum amount of non-expansion work obtainable is equal to G rxn and the change in Gibbs free energy for a chemical reaction is something that can be determined.
G H - T S 2 T is the temperature in Kelvin H is H reaction in Joules or kilojoules S is S reaction in Joules or kilojoules Note. Rxn and ΔG rxn. The standard gives free energy is given by the difference in reacted and product chemical reaction.
The difference between a fast reaction and one that occurs slowly is simply the value of ΔG. Hence if we know H rxn and S rxn we can use the following equation to determine the approximate temperature at which the spontaneity of a. Find grxn in kilojoules when 100 g of calcium oxide is reacted with 250 mL of water to form calcium hydroxide.
If a chemical equation can be expressed as the sum of a series of steps then Grxn for the overall equation is the sum of the free energies of reactions for each step. Grxn G o rxn 2303 RT log Q or Grxn G o rxn RT ln Q. If a chemical equation is multiplied by some factor the Grxn is also multiplied by the same factor.
When Grxn is positive the log of K is negative and K 1. Assume the density and heat capacity of the solution are the same as they are for water. Under equilibrium conditions QK and ΔG 0 so ΔG0 RT lnK.
We have Delta_mathrmrG sum nu_i mu_i. Conversely reactions with low ΔGvalues proceed quickly. H reaction and S reaction must either both be in J or both in kJ Key.
Different from the standard value. The larger the activation energy barrier the more energy must be infused into the substrates before they can become products and therefore the slower the reaction. When Δ H rxn and ΔS rxn are both positive.
Up to 24 cash back Yes the reaction is spontaneous because the value of AGO for the reaction is negative 2572 Id mol-I. The difference between G o and G for a reaction is important. Partial Pressure of gases 01 MPa.
Gibbs free energy G is a state function defined with regard to system quantities only and may be used to predict the spontaneity of a process. AGO rxn -R Tin K eq -257200 J mol. O Discuss possible sources of error that resulted in your values of Grxn being.
When Grxn is zero the log of K is zero and K 1. To your calculated values in lab. After the leaving group leaves the other substituents shift to make room for the newly-bonded nucleophile changing the stereochemistry of the molecule.
Theres an another formula that is Delta G is a Quintal. The reaction happens to be at equilibrium under standard conditions. The standard gives free energy apply for standard condition in case off nonstandard conditions.
For the reaction ce3H2 N2 - 2NH3 we have. From my understanding the naught refers to standard conditions making me think that the only difference between the two values are that delta G naught is the change in free energy in 1 atm and 25 degrees Celsius and delta G is just the change in free energy in any other condition. And a Δ G of zero indicates that the system is at equilibrium.
This means that Delta_mathrmrG is simply the difference between the chemical potentials of the products and the reactants weighted by their stoichiometric coefficients. The relationship between Grxn and K is Grxn -RT lnK. In other words reactions that release energy have a G 0.
Rxn is calculated at any point in the reaction at non-standard conditions. Assume a temperature of 298 K b. Calculate K for the reaction between glutamate and ammonia.
If energy is released during a chemical reaction then the resulting value from the above equation will be a negative number. The relationship between G rxn and G rxn is shown in Equation 3 below. Gibbs free energy also known as the Gibbs function Gibbs energy or free enthalpy is a quantity that is used to measure the maximum amount of work done in a thermodynamic system when the temperature and pressure are kept constant.
Its value is usually expressed in Joules or Kilojoules. What is G rxn and K for the coupled reaction. Under standard conditions Q1 and ΔG ΔG0.
There is only one value of G o for a reaction at a given temperature but there are an infinite number of possible values of G. The temperature of the water increases from 2500 C to 2608 C. This back-side attack causes an inversion study the previous slide.

19 6 Gibbs Energy Change And Equilibrium Chemistry Libretexts

Solved Where Delta G Degree The Standard Free Energy Chegg Com


0 Comments